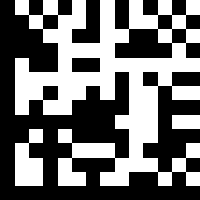1D Bar Codes
Linear bar codes are one-dimensional (1D) codes first used in the 1970s to identify retail products. As computers and other digital devices became more affordable over time, bar codes were adopted and their use became widespread across many industries.
While there are many bar code symbologies used to identify items in retail, healthcare, transportation, and postal systems, there are just a few that are commonly used in industrial manufacturing.

| Symbology |
Code 39
|
Code 128 |
Interleaved 2 of 5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Code 39 (or Code 3 of 9) was the first alphanumeric bar code developed, and it remains widely used today. | Code 128 is a more compact symbology, allowing more characters to be encoded in a small space. | Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF) bar codes are numeric only and are commonly used on labels and packaging. |
| Available Characters | 0–9, A–Z, and special characters – . $ / + % [space] | All 128 standard ASCII characters | 0–9 only |
| Lower Case Characters Allowed | No | Yes | n/a |
| Spaces Allowed | Yes | Yes | No |
| Check Digit | Optional | Required | Optional |
| Encoding Rules | Encoded data must be bounded by an asterisk start and stop character.
Example: *Pannier 123* |
Codes are constructed using start characters to indicate one of three ASCII code sets: 128A, 128B, and 128C | Codes must contain an even number of digits. If encoding a number with an odd number of digits, a leading zero must be added. |
| Further Reading | Code 39 symbology | Code 128 symbology | ITF Code symbology |
2D Codes
Two-dimensional (2D) codes, sometimes called “2D barcodes”, encode data in cells laid out in a horizontal and vertical matrix. These sophisticated symbologies can store 100 times more information than bar codes.
Error Correction
2D codes incorporate duplicate data to ensure readability in case a code is damaged, distorted, or difficult to read. The error checking and correction algorithms ensure a Data Matrix code is still correct with up to 60% damage, and QR code with up to 30% damage.

| Symbology |
Data Matrix
|
QR
|
PDF417
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | A Data Matrix is a square or rectangular matrix of cells.
Cells can be square or circular in shape, allowing the codes to be made by several types of marking systems. |
The QR (Quick Response) was developed in Japan for use in the automotive industry.
There are many types of QR codes, but for industrial applications they are typically encoded to contain text only. |
PDF417 (Portable Data File) is constitutes a series of bar codes stacked on top of each other.
This is the standard code used by the US government and military. |
| Available Characters | All 256 ASCII characters and extended characters | Four input modes/character sets:
Numeric: 0–9 only Alphanumeric: 0–9, upper case A–Z, special characters – . $ / + % : [space] Byte: Latin-1 (ISO 8859-1) Kanji: JIS X 0208 |
All 256 ASCII characters and extended characters |
| Error Correction | Fixed error correction based on the code size. | Four selectable levels of error correction. | Nine selectable levels of error correction. |
| Further Reading | Data Matrix code symbology | QR code symbology | PDF417 code symbology |